XR Digital
At XR Digital, we blend creativity, technology, and strategy to deliver unparalleled digital solutions. Explore the possibilities with us as we push the boundaries of innovation and transform your vision into reality.
In recent years, the convergence of technology and healthcare has ushered in a new era of innovation, with Virtual Reality (VR) emerging as a transformative force at the forefront of this intersection. Virtual Reality, once relegated to the realms of gaming and entertainment, has found a profound purpose within the healthcare landscape.
Its immersive capabilities are reshaping the way medical professionals approach training, patient care, and therapy. By leveraging the power of simulated environments, VR is not merely transporting individuals to fantastical realms; it is transporting healthcare into a realm of unprecedented possibilities.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual reality (VR) are two of the masterpieces in contemporary technology. Eight out of top ten tech companies are invested in and committed to these technologies including Apple, Microsoft, Google, Samsung, Intel, IBM, Foxconn, and HP. AR & VR, both elicit an immediate connection with gaming and entertainment.
This introduction explores the diverse applications of Virtual Reality in healthcare, from revolutionizing medical training to providing novel solutions for patient treatment and rehabilitation. As we delve into the immersive potential of VR, we uncover a landscape where technology meets compassion, offering new avenues for enhanced education, patient engagement, and therapeutic interventions. Welcome to the realm where pixels and empathy converge, reshaping the future of healthcare: Virtual Reality in action.
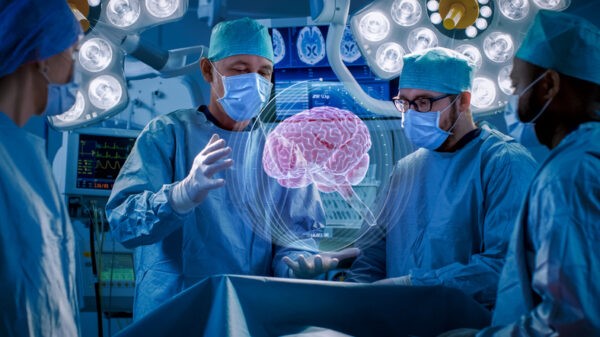
Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare refers to the utilization of computer-generated simulations to create immersive, three-dimensional environments that healthcare professionals and patients can interact with for various purposes. The integration of virtual reality technology in healthcare settings has the potential to enhance medical training, improve patient outcomes, and provide innovative solutions for therapeutic interventions.
When you put on a motion-sensing VR headset (and sometimes handheld controllers), your surroundings vanish. It is immediately replaced with a 360-degree virtual world into which you may enter, move around, and engage.
The experience feels real, and your brain processes it that way. If you need distraction from pain or stress, you may find yourself beneath the ocean, surrounded by dolphins. As you float along, you can look up and see the sun shining through the water’s surface. Look down and you see dolphins swimming around and below you. You can hear the echo of the underwater world and the sounds of the big mammals that surround you.
The applications of virtual reality in healthcare are diverse and rapidly expanding, offering innovative solutions to improve patient care, medical training, and therapeutic interventions.
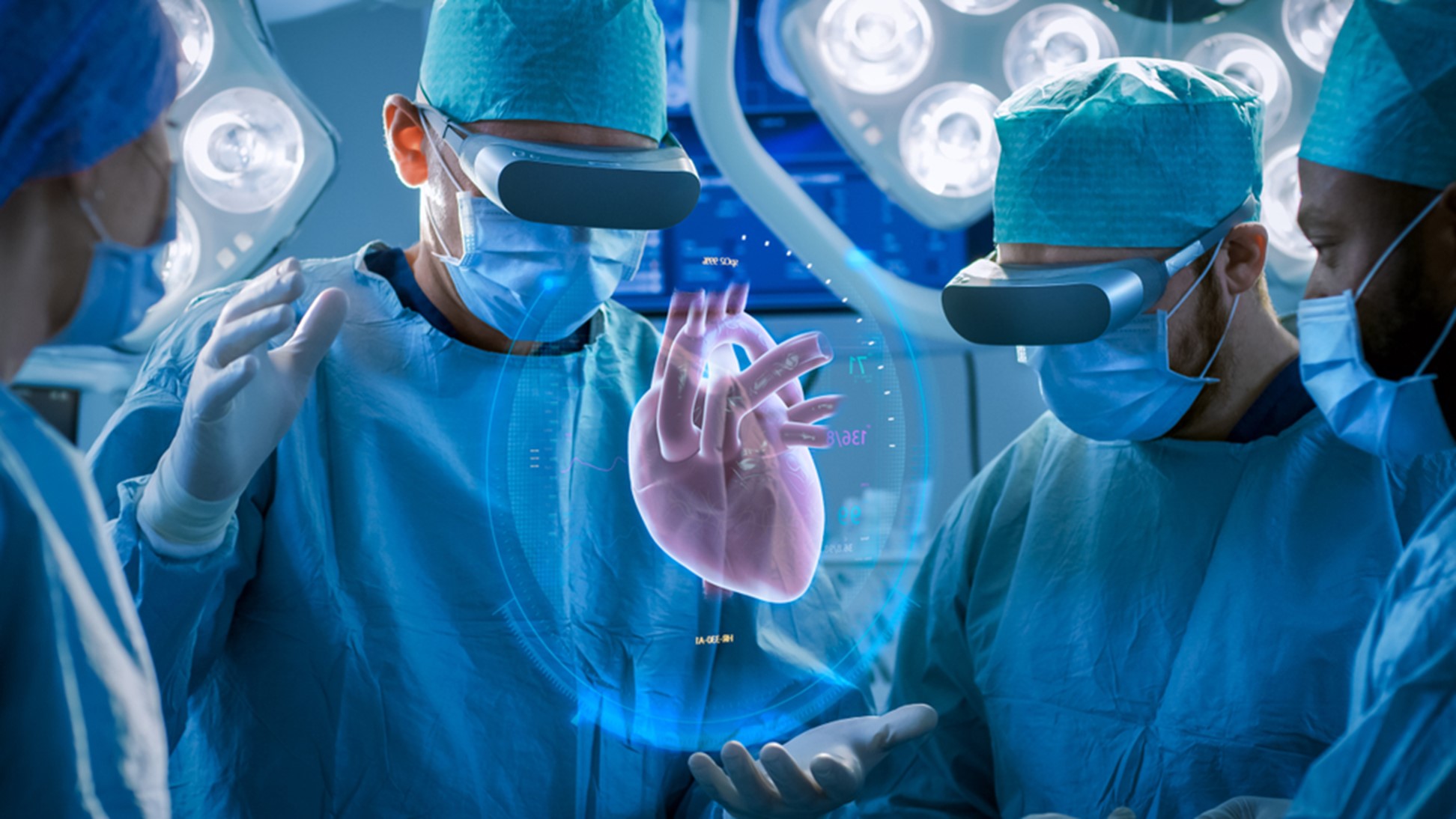
Virtual Reality (VR) has revolutionized medical training and education, offering a dynamic platform for healthcare professionals to enhance their skills and knowledge. Surgeons, in particular, benefit from hands-on practice in a controlled virtual environment, allowing them to refine their techniques for complex procedures.
Medical students delve into the intricacies of anatomy through three-dimensional exploration, providing a comprehensive and immersive learning experience. Additionally, healthcare providers sharpen their diagnostic skills by engaging with virtual patient cases, ensuring a well-prepared and competent medical workforce.
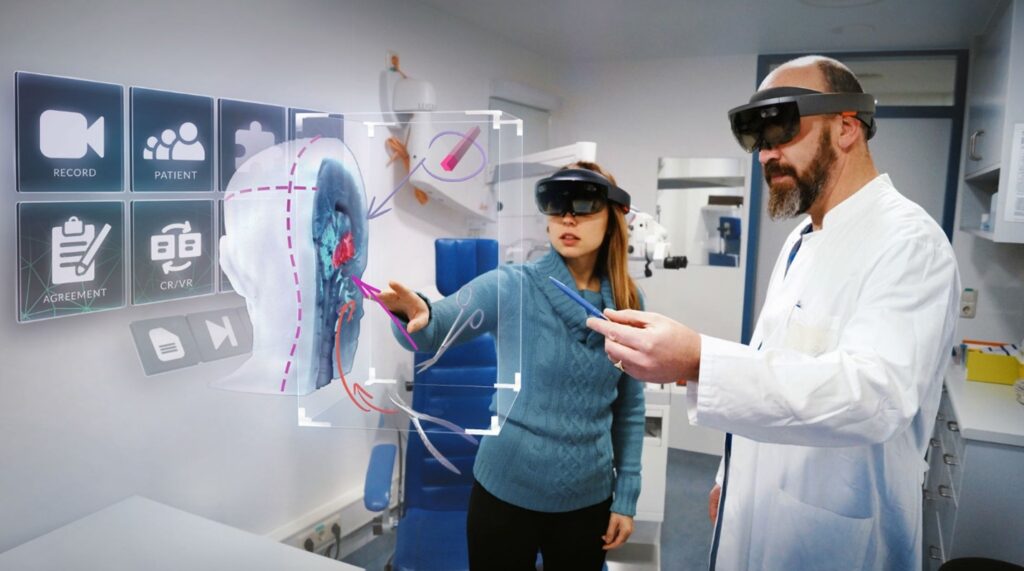
VR serves as a powerful tool in patient education, providing individuals with a unique opportunity to visualize medical procedures and treatment options. Patients facing surgeries can use VR to immerse themselves in a virtual representation of the procedure, alleviating anxiety and fostering a better understanding of the process. This form of education empowers patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare, contributing to improved treatment outcomes. By bridging the gap between medical professionals and patients, VR plays a pivotal role in creating a more informed and engaged healthcare community.
VR can help patients improve their physical functions and mobility after a stroke, brain injury, spinal cord injury, or other medical condition.
With VR-based physical therapy and rehabilitation, therapists can choose software that helps the patient improve specific skills and targets individual problems. VR can simulate real-life situations and provide feedback and motivation to help patients practice their skills and achieve their goals.
Children with CRPS may experience agony every day of their lives. The therapist may employ a VR rehabilitation software in which they perform certain movements to squash watermelons. They can participate more fully in rehabilitation since they are now more focused on squashing those watermelons rather than on their agony.
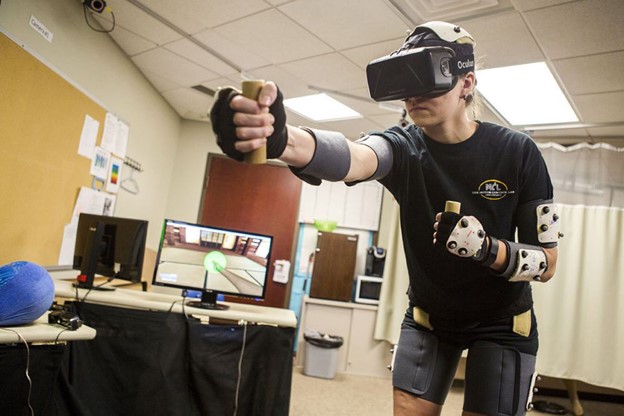

Telemedicine has seen significant advancements with the integration of virtual reality technologies. VR enhances remote consultations by creating immersive virtual environments, allowing physicians to interact with patients on a more personalized level. Remote surgeries are facilitated through VR, with physicians utilizing the technology in conjunction with robotic systems. This not only ensures access to healthcare services in remote or critical situations but also minimizes the need for physical presence, thus transforming the landscape of telemedicine.
VR for pain control is one of the best-studied and most-used applications of the technology. Doctors have known for decades that this technological “distraction therapy” is an effective tool to combat pain and the fear of pain.
“Pain is a perception that’s coupled to your attention, mood, and emotions,”
VR can help reduce pain and anxiety by distracting the user from negative stimuli and creating a sense of presence in a virtual world. VR can be used along with medication to enhance pain relief for patients with acute or chronic pain, such as burn injuries, cancer, or fibromyalgia.
With VR, we can help modulate a patient’s mindset to be less focused on pain and anxiety.

Virtual reality’s impact extends to the realm of medical research and development, where it serves as a catalyst for innovation. Researchers leverage VR to simulate experiments, test hypotheses, and visualize complex data sets. The ability to immerse themselves in virtual environments accelerates the pace of discovery, leading to advancements in treatments, drugs, and medical technologies. As a result, virtual reality not only transforms patient care but also propels the healthcare industry forward through continuous research and development efforts.
Chemotherapy is a stressful and sometimes uncomfortable experience. Some medical centers now use VR to help their patients escape from anxiety or the boredom of treatments that can take hours.
VR can help patients cope with fear and stress before, during, or after a medical procedure, such as surgery, dental treatment, or blood draw. VR can provide relaxation, education, or exposure therapy to help patients overcome their phobias and increase their confidence.
Kids think of it like a video game. They use a joystick to zoom in through corridors in their brain, look at their tumor, and view things upside down. It brings kids into the process and takes away some of their fear.
VR can widely help in Marketing and Communication. VR can help healthcare providers and organizations promote their products and services, educate their customers and stakeholders, and enhance their brand image. VR can also help patients and their families understand their medical condition or treatment options and make informed decisions.
VR is still in its early days as far as medical applications are concerned. In the future, VR is likely to be increasingly used to enhance the safety and efficacy of surgical procedures, especially those which are minimally invasive or non-invasive, and to better understand the intricacies of the human body.
VR can help create and manipulate 3D models of organs and tissues, using data from medical imaging, such as MRI, CT, or ultrasound. VR can help researchers and engineers design and test new biomaterials, scaffolds, and bioreactors, and optimize the growth and function of engineered tissues. VR can also help surgeons implant and monitor the engineered organs and tissues in patients.
Implementing Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare presents a set of challenges and considerations that need careful attention. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure the effective integration of VR technology into medical settings. Here are key challenges and considerations:

As conclude this it is evident that the convergence of technology and compassion in the form of Virtual Reality holds immense promise for the future of healthcare. This is a realm where the pixels on a screen become pathways to healing, education, and empowerment, ultimately reshaping the very fabric of how we perceive and deliver healthcare services.
The journey has just begun, and the horizon is filled with possibilities as Virtual Reality continues to unfold its transformative potential in the world of healthcare. Welcome to a future where pixels and empathy converge, reshaping the very essence of healthcare delivery Virtual Reality in action.
If you loved the article you might want to learn Virtual Reality in medicine and Virtual Reality in social media.

In the rapidly advancing landscape of healthcare technology, the transformative power of virtual reality (VR) stands out prominently, offering innovative solutions that align with XR Digital’s commitment to cutting-edge services. XR Digital, with its expertise in immersive technologies, is well positioned to leverage these advancements, contributing to the evolution of Digital World.
XR Digital offers its innovative services in Virtual Reality. XR Digital, with its commitment to cutting-edge technology, is positioned as a key player in shaping the future of the immersive Digital World, echoing the sentiments expressed in the exploration of VR’s applications in different businesses.
VR is used in medical training to simulate realistic environments for practicing surgeries, medical procedures, and diagnostic skills. It provides a safe and controlled space for healthcare professionals to enhance their skills.
Yes, VR is utilized for patient education by creating immersive experiences that help individuals better understand their medical conditions, treatment options, and procedures. It enhances patient engagement and knowledge.
VR allows surgeons to visualize and plan complex surgeries by interacting with 3D models of a patient’s anatomy. This enhances precision, improves preoperative planning, and contributes to better surgical outcomes.
VR is used as a distraction tool for patients undergoing painful procedures or experiencing chronic pain. Immersive experiences created by VR can reduce the perception of pain and create a more pleasant environment.
Yes, VR is employed in mental health treatments, including exposure therapy for phobias, PTSD, and anxiety disorders. It provides a controlled environment for patients to confront and overcome their fears.
At XR Digital, we blend creativity, technology, and strategy to deliver unparalleled digital solutions. Explore the possibilities with us as we push the boundaries of innovation and transform your vision into reality.